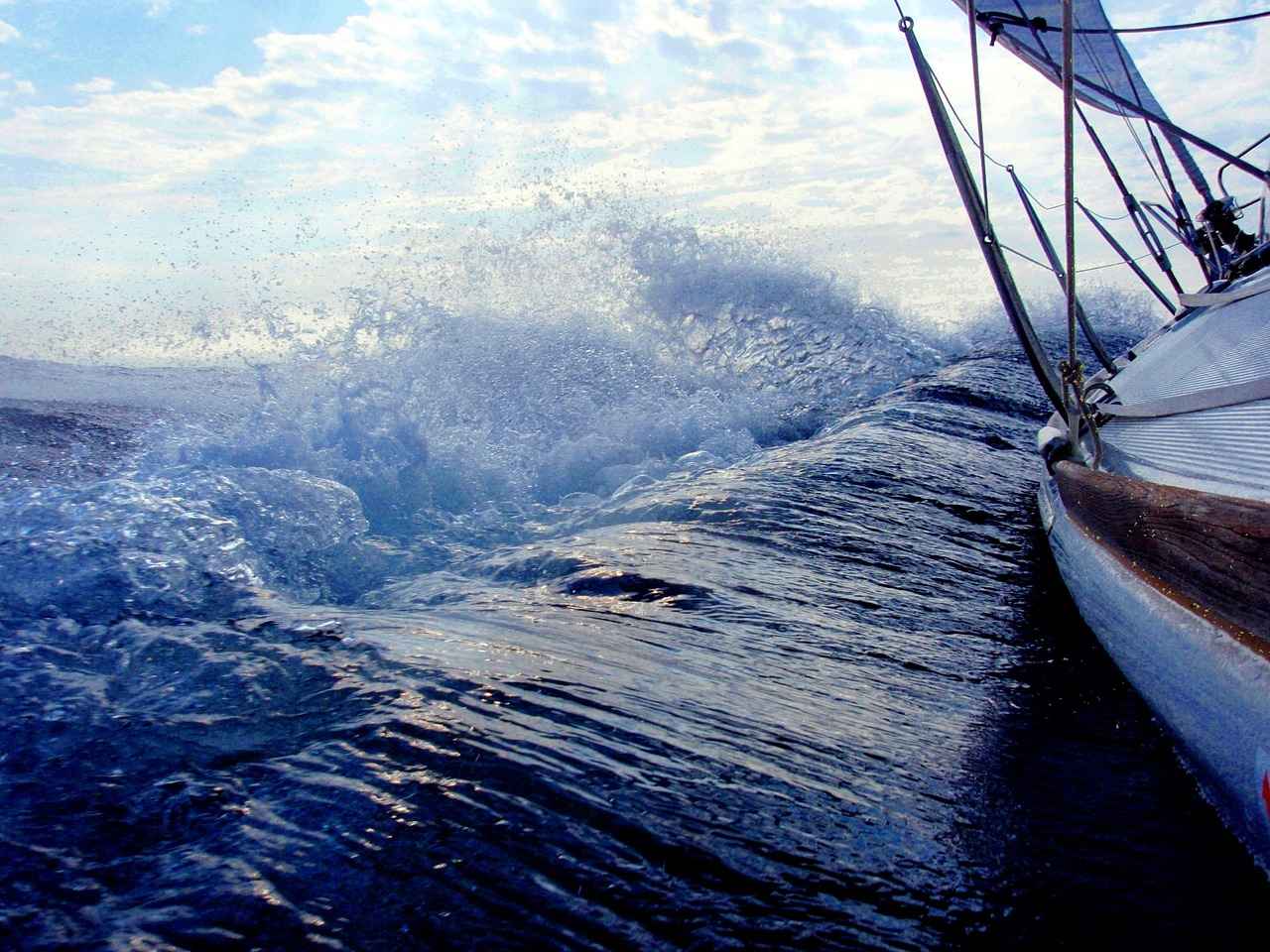
This article delves into the various elements that influence the duration of a sailing journey around the globe. By examining factors such as boat type, routes, and sailing conditions, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the time it typically takes for sailors to complete this remarkable adventure.
What Factors Influence Sailing Time Around the World?
Estimating the time it takes to circumnavigate the globe requires a grasp of key factors that affect sailing time. These include:
- Boat Type: Different vessels have unique speeds and capabilities.
- Weather Conditions: Wind patterns and storms can dramatically alter sailing times.
- Sailing Routes: The chosen path can either expedite or prolong the journey.
How Does Boat Type Affect Sailing Duration?
The type of boat significantly impacts the overall duration of a global sailing journey. For instance:
- Sailboats: Racing yachts can achieve higher speeds compared to cruising sailboats, which may take longer due to their design.
- Catamarans vs. Monohulls: Catamarans often offer greater stability and speed, potentially reducing travel time.
- Hull Design: The hydrodynamics of a boat’s hull can greatly influence its efficiency and speed over long distances.
What Are the Speed Differences Among Sailboats?
Speed variations among sailboats can be substantial. Racing yachts can often sail at speeds of 15 knots or more, while cruising sailboats typically average between 4 to 8 knots. This disparity can lead to significant differences in the time taken to complete a global journey.
What Role Does Motorboats Play in Sailing Duration?
Motorboats typically have higher average speeds than sailboats, often reaching around 20 knots. However, fuel considerations and operational costs may lead sailors to prefer sailboats for long journeys.
How Do Weather Conditions Impact Sailing Times?
Weather plays a pivotal role in sailing durations. Key considerations include:
- Best Seasons for Sailing: Understanding seasonal weather patterns can help sailors choose the optimal time for their journey, potentially reducing travel time.
- Storms and Weather Systems: Navigating around storms can significantly alter planned routes, affecting overall journey duration.
What Are the Most Common Sailing Routes?
The choice of sailing route can greatly influence the time taken to sail around the world. Popular paths include:
- The Traditional Clipper Route: This route offers favorable winds and currents, making it a popular choice among sailors.
- Alternative Routes: Routes like the Panama or Suez Canals can save time but may involve additional fees and logistical planning.
What Is the Average Time to Sail Around the World?
Estimating the average time to complete a circumnavigation generally falls between 1 to 3 years for experienced sailors. In contrast, novice sailors may take longer, often between 3 to 5 years, as they navigate learning curves and adapt to the challenges of long-distance sailing.
What Are the Key Preparations for a Global Sailing Journey?
Before embarking on a journey around the world, thorough preparations are essential. Key considerations include:
- Necessary Equipment: Proper navigation tools, safety gear, and communication devices are crucial for a successful circumnavigation.
- Crew Experience and Training: A well-trained crew can enhance sailing efficiency and safety, ultimately affecting the time taken to complete the journey.
In conclusion, the time it takes to sail around the world is influenced by a myriad of factors including boat type, weather conditions, and chosen routes. By understanding these elements, sailors can better estimate their journey and prepare accordingly.

What Factors Influence Sailing Time Around the World?
Sailing around the world is a thrilling adventure that beckons many nautical enthusiasts. However, estimating the time it takes to complete such a journey involves a myriad of factors. Understanding these factors is essential for anyone considering a global sailing expedition. This article delves into the key elements that influence sailing time, including boat type, weather conditions, and sailing routes.
When planning a circumnavigation, several critical factors come into play:
- Boat Type: Different vessels possess unique characteristics that affect speed and handling.
- Weather Conditions: Wind patterns, storms, and seasonal changes can drastically alter sailing times.
- Sailing Routes: The chosen path can either expedite or prolong the journey due to geographical and environmental challenges.
The type of boat is perhaps the most significant factor in determining how long it will take to sail around the world. Various designs cater to different sailing styles and conditions:
- Sailboats: Racing yachts can reach impressive speeds, often completing the journey faster than cruising sailboats, which prioritize comfort over speed.
- Catamarans vs. Monohulls: Catamarans typically offer greater stability and speed, which can shorten travel time compared to traditional monohulls.
- Motorboats: With generally higher speeds, motorboats can complete the journey in a fraction of the time, but fuel costs and logistics must be considered.
Weather plays a crucial role in sailing durations. Sailors must be adept at reading weather patterns and adjusting their plans accordingly:
- Optimal Seasons: Choosing to sail during favorable seasons can significantly reduce travel time. For instance, the trade winds can aid in faster passages across the oceans.
- Storm Navigation: Avoiding storms and adverse weather systems is essential. They not only pose safety risks but can also delay progress due to detours.
The route taken can greatly influence the overall duration of the journey. Some popular routes include:
- The Clipper Route: Historically favored for its advantageous winds and currents, this route remains a popular choice for modern sailors.
- Alternative Routes: Utilizing canals like the Panama or Suez can save time, but they involve additional logistical considerations and fees.
The average duration to complete a circumnavigation varies widely:
- Experienced Sailors: Typically, they complete the journey in about 1 to 3 years, depending on their chosen route and sailing style.
- Novice Sailors: Those new to sailing may take longer, often ranging from 3 to 5 years, as they learn and adapt to the demands of long-distance sailing.
Preparation is paramount for a successful circumnavigation. Key considerations include:
- Essential Equipment: Navigation tools, safety gear, and communication devices are crucial for ensuring a safe and efficient journey.
- Crew Experience: A well-trained crew can enhance sailing efficiency and safety, ultimately influencing the overall time taken to complete the journey.
In summary, understanding the factors that influence sailing time around the world is vital for anyone planning such an adventure. From the type of boat to the weather and chosen routes, each element plays a significant role in determining the duration of this extraordinary journey.
How Does Boat Type Affect Sailing Duration?
When planning a global sailing journey, one of the most critical factors to consider is the type of boat being used. Different boats come with unique designs, speed capabilities, and handling characteristics that can significantly affect the duration of the journey. Understanding these differences can help sailors make informed decisions about their voyage.
Speed Variations Among Different Boat Types
Boats can be classified into several categories, each with varying speeds:
- Sailboats: These vessels are designed for wind propulsion and can vary widely in speed. Racing yachts can reach speeds of over 20 knots, while cruising sailboats typically average between 5 to 8 knots.
- Motorboats: Generally faster than sailboats, motorboats can cruise at speeds of 20 to 30 knots, making them ideal for quicker journeys. However, fuel consumption and operational costs can be significant drawbacks.
- Catamarans: Known for their stability and speed, catamarans can often sail faster than monohulls, particularly in rough seas, which can reduce overall travel time.
Impact of Hull Design on Speed
The hull design of a boat plays a crucial role in its hydrodynamics. A well-designed hull can cut through water more efficiently, allowing for higher speeds and better fuel economy. For example:
- Monohulls: These boats typically have a single hull and can be slower due to their design, which may not be as aerodynamic.
- Multihulls: Catamarans and trimarans, which have multiple hulls, often achieve greater speeds due to their reduced water resistance.
Considerations for Different Sailing Styles
The type of sailing style also impacts how long it takes to complete a journey:
- Leisurely Cruising: Sailors who prefer a relaxed pace may take longer, as they might stop frequently to explore various ports and attractions.
- Racing: Competitive sailors aim for the fastest routes and utilize strategies to maximize speed, significantly reducing travel time.
Weather and Its Influence on Boat Performance
The performance of a boat is not solely dependent on its type; weather conditions also play a vital role. Wind patterns, currents, and storms can either enhance or hinder sailing speed. For example:
- Favorable Winds: Boats can sail faster with strong, consistent winds, especially sailboats that rely on wind power.
- Adverse Conditions: Heavy storms or unfavorable winds can slow down progress, requiring sailors to adjust their routes and strategies.
Conclusion
In summary, the type of boat significantly influences the duration of a global sailing journey. By understanding the various capabilities and characteristics of different boats, sailors can make informed decisions that will affect their overall experience and travel time. Whether opting for a sleek racing yacht or a sturdy cruising sailboat, each choice comes with its own set of advantages and challenges that can shape the adventure of sailing around the world.
What Are the Speed Differences Among Sailboats?
Sailing is a captivating adventure that attracts enthusiasts from all walks of life. One of the most intriguing aspects of sailing is the speed differences among sailboats, which can significantly influence the overall duration of a journey, especially when considering a global circumnavigation. Understanding these differences is essential for anyone planning such an ambitious endeavor.
Several factors contribute to the varying speeds of sailboats, including:
- Design and Type: The design of a sailboat’s hull and its type—racing yachts versus cruising sailboats—play crucial roles in speed. Racing yachts are engineered for speed, often featuring sleek hulls and lightweight materials.
- Wind Conditions: The amount and direction of wind can dramatically affect a sailboat’s speed. Optimal wind conditions can propel a racing yacht to impressive speeds, while cruising sailboats may require more favorable winds to maintain a decent pace.
- Weight and Load: The weight of the boat, including its cargo and crew, can impact its speed. Lighter vessels generally sail faster, while heavier boats may struggle to achieve high speeds.
- Keel Design: The shape and type of keel can influence a sailboat’s stability and speed. A well-designed keel can enhance performance, allowing for faster sailing.
Racing yachts are purpose-built for speed and competition, often reaching speeds of 20 knots or more under ideal conditions. In contrast, cruising sailboats typically average around 5 to 8 knots, designed for comfort and stability rather than outright speed. This difference in speed can lead to significant variations in journey duration.
Catamarans, with their twin hulls, offer advantages in both stability and speed compared to traditional monohulls. Many catamarans can sail at speeds comparable to racing yachts, often exceeding 15 knots. This speed advantage can make a considerable difference in the time it takes to complete a global circumnavigation.
The hull design of a sailboat is a critical factor in determining its speed and efficiency. A streamlined hull reduces drag, allowing the boat to glide more smoothly through the water. Conversely, a poorly designed hull can create turbulence, slowing the vessel down. Sailors should consider hull design carefully when selecting a boat for long-distance sailing.
While the focus here is on sailboats, it’s worth noting that motorboats generally have higher average speeds than sailboats. Many motorboats can cruise at speeds exceeding 20 knots, which can lead to significantly shorter sailing durations. However, motorboats come with their own set of challenges, including fuel costs and environmental considerations.
When planning a sailing journey, especially one around the world, understanding the speed of your vessel is vital. A faster sailboat may allow for more flexibility in route selection, potentially reducing travel time. Conversely, a slower sailboat may require more careful planning to account for weather conditions and the time needed to reach various destinations.
In conclusion, the speed differences among sailboats are influenced by various factors, including design, weight, and environmental conditions. Racing yachts typically outpace cruising sailboats, while catamarans offer a unique blend of speed and stability. Understanding these dynamics can help sailors make informed decisions about their vessels and journey planning.
How Do Catamarans Compare to Monohulls?
Sailing enthusiasts often find themselves debating the merits of different boat types, particularly catamarans and monohulls. When it comes to circumnavigating the globe, the choice of vessel can significantly influence not only the experience but also the time required to complete the journey.
One of the primary advantages of catamarans is their speed. Typically, catamarans have two hulls, which allows them to glide over the water with less drag compared to monohulls, which have a single hull. This design enables catamarans to achieve higher average speeds, particularly in favorable wind conditions. As a result, sailors can cover greater distances in shorter periods.
In addition to speed, stability is a crucial factor that sets catamarans apart. Their wide beam and dual-hull design provide a stable platform, reducing the likelihood of heeling (the tilting of the boat). This stability is particularly beneficial during long voyages, where rough seas can pose challenges. Sailors aboard catamarans often report a more comfortable ride, which can lead to increased efficiency in sailing and reduced fatigue.
Weather can be unpredictable, and choosing the right vessel to navigate through various conditions is essential. Catamarans generally perform better in strong winds and choppy waters, allowing sailors to maintain speed and control. In contrast, monohulls may struggle with stability in similar conditions, potentially leading to slower speeds and longer travel times.
The combination of speed and stability in catamarans can significantly affect the overall duration of a circumnavigation. Sailors can plan more ambitious routes, taking advantage of favorable winds and currents without the fear of excessive heeling or capsizing. This ability to maintain a consistent pace can reduce the total time spent at sea, making catamarans an appealing choice for those aiming to complete a global journey efficiently.
While catamarans offer numerous advantages, it’s essential to consider potential trade-offs. They can be more expensive to purchase and maintain compared to monohulls. Additionally, their wider beam may limit access to certain harbors and marinas. However, many sailors find that the benefits of speed and stability outweigh these drawbacks, especially for long-distance sailing.
Comfort is another critical aspect of long-distance sailing. Catamarans typically provide more living space and amenities due to their larger size and dual-hull configuration. This extra space can enhance the overall experience, allowing for better storage, cooking facilities, and sleeping arrangements. Sailors can enjoy a more comfortable lifestyle while at sea, which can be particularly beneficial during extended voyages.
In summary, the choice between a catamaran and a monohull can profoundly affect the time and experience of circumnavigating the globe. With their superior speed, stability, and comfort, catamarans often emerge as the preferred vessel for many sailors. However, understanding the trade-offs and practical implications is essential for making an informed decision that aligns with individual sailing goals.
What Role Does Hull Design Play in Speed?
The design of a boat’s hull plays a crucial role in its overall performance, particularly in terms of speed and efficiency. A well-designed hull can significantly enhance a vessel’s hydrodynamics, allowing it to glide through water with minimal resistance. This article delves into the various aspects of hull design and how it impacts sailing speed.
The hull of a boat is its main body, and its shape is engineered to interact with water effectively. Factors such as length, width, and shape all contribute to how a hull performs. For instance, a longer hull generally offers better speed potential due to reduced water resistance, while a wider hull can provide more stability but may sacrifice some speed.
Hull shape is a critical determinant of a boat’s hydrodynamic efficiency. There are several common hull shapes:
- Displacement Hulls: These hulls push water aside and are typically found on cruising sailboats. They are slower but offer stability and comfort.
- Planing Hulls: These hulls lift out of the water at higher speeds, reducing drag. They are common in racing boats and speedboats, allowing for faster travel.
- Catamaran Hulls: Featuring two parallel hulls, catamarans provide excellent stability and can achieve higher speeds than monohulls due to reduced drag.
The materials used in hull construction also influence speed. Lightweight materials such as fiberglass and carbon fiber allow for faster acceleration and improved maneuverability. In contrast, heavier materials like steel may enhance durability but can slow down the vessel.
In addition to speed, hull design significantly affects fuel efficiency, especially for motorboats. A streamlined hull that minimizes drag can lead to lower fuel consumption, allowing for longer voyages without the need for frequent refueling. This efficiency is vital for long-distance sailing, where fuel costs can add up quickly.
The keel is another essential component of hull design. It provides stability and prevents sideways drift during sailing. The shape and depth of the keel can influence the boat’s speed and handling. For example:
- Shallow Keels: These are often found on cruising boats and allow for easier navigation in shallow waters but may not perform as well in terms of speed.
- Deep Keels: More common in racing boats, deep keels enhance stability and speed, allowing the boat to cut through water more efficiently.
The relationship between hull design and sail area is also significant. A boat with a well-balanced hull can effectively utilize its sail area, maximizing speed and efficiency. Conversely, an ill-suited hull may lead to poor performance, even with a large sail area.
In summary, the design of a boat’s hull is a fundamental aspect that influences its speed and efficiency during long voyages. By understanding the various elements of hull design, sailors can make informed decisions about their vessels, optimizing performance for their specific sailing needs.
What Are the Considerations for Motorboats?
When considering a global sailing adventure, one must weigh the advantages and disadvantages of different types of vessels. Motorboats and sailboats each offer unique benefits, but they also come with distinct considerations that can significantly impact the journey’s overall experience and duration.
Motorboats are known for their higher average speeds compared to sailboats. This speed advantage can lead to significantly shorter sailing durations, making them an appealing choice for those looking to complete a circumnavigation in less time. For instance, while a sailboat might average around 5-7 knots, motorboats can easily reach speeds of 15 knots or more, depending on the model and conditions.
Despite their speed, motorboats come with fuel considerations that can affect the overall cost of the journey. Unlike sailboats that primarily rely on wind, motorboats require fuel, which can be expensive and may not always be readily available in remote locations. This reliance on fuel can also affect planning, as sailors must consider refueling stops along their route.
In addition to fuel, motorboats typically incur higher operational costs. Maintenance, insurance, and docking fees can add up quickly. Sailboats, on the other hand, often have lower maintenance costs and can be more economical over time. Therefore, it is essential for potential sailors to evaluate their budget and long-term plans when choosing between these two vessel types.
Another aspect to consider is the environmental impact of motorboats. The emissions from fuel consumption can contribute to pollution, making some sailors prefer the eco-friendliness of sailboats. This consideration is becoming increasingly important for many sailors who are conscious of their carbon footprint.
While both motorboats and sailboats require skill, operating a motorboat can sometimes be more straightforward, particularly for those who may not have extensive sailing experience. However, understanding navigation, weather patterns, and safety protocols remains crucial for all types of vessels, ensuring a safe and enjoyable journey.
Weather can significantly impact the performance of motorboats. Unlike sailboats that can harness wind power, motorboats must contend with rough seas and adverse weather conditions that can affect speed and fuel efficiency. Sailors must be prepared to adjust their plans based on weather forecasts, which can lead to delays or changes in routes.
- Regular Maintenance: Ensure that the motor is well-maintained and serviced regularly to prevent breakdowns.
- Fuel Management: Keep track of fuel levels and plan refueling stops in advance.
- Weather Monitoring: Continuously monitor weather conditions and be prepared to change course if necessary.
- Safety Equipment: Equip the boat with necessary safety gear, including life jackets, flares, and first aid kits.
In conclusion, while motorboats offer the advantage of speed and shorter sailing durations, they come with considerations that sailors must carefully evaluate. From fuel costs to environmental impacts, understanding these factors will help ensure a successful and enjoyable journey around the world.

How Do Weather Conditions Impact Sailing Times?
Sailing around the world is a thrilling adventure, but it is heavily influenced by various weather conditions. Understanding how these factors can affect sailing times is essential for any sailor planning a global journey. This article delves into the impact of weather patterns, wind conditions, and storms on sailing durations.
Weather conditions are not just a minor detail; they are a critical determinant of how long it takes to sail around the globe. Key factors include:
- Wind Patterns: Consistent and favorable winds can significantly speed up a sailing journey, while adverse winds can slow it down.
- Storms: Encountering storms can lead to detours, delays, and sometimes dangerous situations, impacting overall travel time.
- Current Conditions: Ocean currents can either aid or hinder progress, depending on their direction and strength.
Wind is the lifeblood of sailing. Understanding wind patterns can drastically alter a sailor’s journey time. For example:
- Trade Winds: These consistent winds blow from east to west and are ideal for eastbound circumnavigation.
- Westerlies: Found in the mid-latitudes, these winds can be beneficial for westward sailing.
Planning a route that takes advantage of these patterns can save valuable time.
Timing is everything in sailing. Different seasons bring varying weather conditions, which can greatly influence sailing times:
- Summer Months: Generally, summer offers more stable weather, making it a popular choice for long voyages.
- Hurricane Season: Sailors should avoid planning trips during this time, as storms can severely disrupt travel plans.
Storms can be a sailor’s worst nightmare. They not only pose safety risks but also lead to significant changes in planned routes:
- Detours: To avoid storms, sailors may need to take longer routes, adding days or weeks to their journey.
- Delays: Waiting out a storm can halt progress entirely, requiring careful planning and flexibility.
Ocean currents can either be a sailor’s ally or adversary. Understanding them is crucial:
- Favorable Currents: Sailing with the current can enhance speed and reduce travel time.
- Adverse Currents: Conversely, sailing against a strong current can lead to slower speeds and increased fuel consumption for motorboats.
Accurate weather forecasting is essential for successful sailing. Sailors should:
- Monitor Weather Reports: Regularly checking forecasts can help in making informed decisions.
- Use Reliable Tools: Employing navigation tools and apps can provide real-time updates on changing weather conditions.
In conclusion, weather conditions are a fundamental aspect of sailing that can drastically affect the time it takes to circumnavigate the globe. By understanding and planning for these variables, sailors can enhance their journey and ensure a safer, more efficient sailing experience.
What Are the Best Seasons for Sailing?
Sailing is a thrilling adventure that many enthusiasts dream of undertaking. However, to ensure a successful journey, it is essential to understand the best seasons for sailing. This knowledge not only enhances the sailing experience but also helps in planning the journey more effectively.
Choosing the right season can significantly impact your sailing experience. Different regions have unique weather patterns that can either facilitate or hinder your journey. Here are some key considerations:
- Spring (March to May): This season often brings mild weather and stable winds, making it an ideal time for sailing. Many sailors prefer to set off during this period to avoid the extreme conditions of summer and winter.
- Summer (June to August): While summer offers long daylight hours, it can also present challenges such as storms and unpredictable weather. Sailors must be prepared for sudden changes in weather patterns during these months.
- Autumn (September to November): Early autumn is often a favorable time for sailing, particularly in temperate regions. The weather is generally stable, and winds are usually favorable, allowing for smooth sailing.
- Winter (December to February): Winter sailing can be challenging due to cold temperatures and harsh weather. However, in tropical regions, this can be the peak sailing season, attracting many sailors to warmer waters.
Understanding seasonal weather patterns is crucial for sailors. Each season presents unique challenges and opportunities:
- Wind Patterns: Different seasons bring varying wind patterns. For instance, trade winds are prevalent in tropical regions during specific months, providing excellent conditions for sailing.
- Storms: Certain seasons are notorious for storms. For example, hurricane season in the Atlantic can pose significant risks to sailors, making it essential to plan routes carefully.
- Temperature Variations: Temperature can affect not only comfort but also the performance of the vessel. Warmer temperatures can lead to better sailing conditions, while colder temperatures may require additional gear and preparation.
Choosing the wrong season for sailing can have serious implications:
- Increased Risks: Sailing during adverse weather conditions can lead to dangerous situations, including capsizing and equipment failure.
- Longer Travel Times: Unfavorable winds and storms can force sailors to take longer routes, significantly extending travel times.
- Higher Costs: Additional fuel costs and potential repairs due to harsh conditions can increase the overall expense of the journey.
Preparation is key to navigating seasonal changes effectively:
- Research: Always stay informed about the weather patterns in your intended sailing area. Utilize weather apps and local forecasts to make informed decisions.
- Flexibility: Be prepared to adjust your plans based on changing weather conditions. Flexibility can make a significant difference in your overall experience.
- Safety Gear: Ensure you have the appropriate safety gear for the season. This includes life jackets, emergency kits, and weatherproof clothing.
In summary, understanding the best seasons for sailing is vital for any sailor. By considering seasonal weather patterns, preparing adequately, and choosing the optimal time for your journey, you can enhance your sailing experience while minimizing risks and travel time.
How Do Storms and Weather Systems Affect Routes?
When planning a global sailing adventure, one of the most crucial factors to consider is how storms and adverse weather systems can impact your journey. Not only do these elements influence safety, but they also play a significant role in altering your planned routes and overall travel duration.
Weather conditions are unpredictable, and sailors must remain vigilant. Storms can arise suddenly, forcing sailors to adjust their routes to avoid dangerous conditions. This can lead to longer travel times, as detours may be necessary to navigate around severe weather systems.
When storms are forecasted, sailors must make quick decisions. Here are some factors to consider:
- Safety First: The primary concern during a storm is the safety of the crew and vessel. This often means taking longer routes that are less exposed to high winds and heavy seas.
- Weather Forecasts: Reliable weather information is essential. Sailors should utilize advanced forecasting tools to anticipate storm paths and adjust their routes accordingly.
- Current Conditions: While planning is vital, real-time weather updates can necessitate immediate changes to the planned route.
In addition to storms, other adverse weather conditions can complicate sailing:
- Strong Currents: Heavy rains and storms can create strong currents that affect speed and direction.
- Wind Patterns: Unfavorable wind conditions can slow down progress, making it necessary to seek alternative routes.
- Fog and Visibility: Reduced visibility due to fog can require slower navigation, impacting the overall duration of the journey.
To mitigate the impact of storms and adverse weather, sailors should:
- Have Flexible Itineraries: A rigid schedule can lead to stress and unsafe decisions. Flexibility allows sailors to adapt to changing conditions.
- Invest in Navigation Technology: Utilizing GPS and weather apps can provide real-time data, helping sailors make informed decisions on the fly.
- Learn from Experienced Sailors: Insights from seasoned sailors can provide valuable tips on navigating around storms and adverse weather.
While storms and adverse weather systems can pose significant challenges for sailors, understanding their impact on routes and journey duration is essential. By planning ahead, remaining flexible, and utilizing technology, sailors can navigate around these challenges more effectively. Ultimately, embracing the unpredictability of weather can lead to a safer and more rewarding sailing experience.

What Are the Most Common Sailing Routes?
When planning a journey around the world, the choice of sailing route holds significant importance. It not only affects the duration of the voyage but also presents various challenges and advantages that sailors must consider. Understanding these popular paths can help sailors make informed decisions that align with their sailing goals and capabilities.
The most common sailing routes are well-trodden paths that experienced sailors have utilized for generations. Each route offers unique characteristics that can influence the overall sailing experience.
- The Clipper Route: This traditional route is favored for its favorable winds and currents, making it a popular choice among circumnavigators. Historically used by clipper ships, it spans from the British Isles around the Cape of Good Hope and across the Pacific Ocean.
- The Panama Canal: This route significantly shortens the distance for sailors traveling between the Atlantic and Pacific Oceans. However, it comes with fees and logistical considerations that must be planned for.
- The Suez Canal: For those navigating from the Mediterranean Sea to the Indian Ocean, this canal offers a direct passage, but like the Panama Canal, it requires careful planning and incurs costs.
- The Cape Horn Route: This challenging route around the southern tip of South America is known for its treacherous waters and unpredictable weather. It is less commonly chosen due to the risks involved but offers a sense of adventure.
The duration of a sailing trip can be heavily influenced by the chosen route. For instance, the Clipper Route typically allows for a faster voyage due to its prevailing winds. In contrast, routes that involve navigating through canals may save time but require additional planning and time at ports.
Popular sailing routes often come with established knowledge and resources that can enhance the sailing experience:
- Established Waypoints: Many common routes have well-documented waypoints, making navigation easier for sailors.
- Access to Marinas: Popular routes often provide access to marinas and ports that offer essential services and supplies.
- Community Support: Choosing a well-known route allows sailors to connect with other sailors, sharing experiences and advice along the way.
While popular routes present numerous advantages, they also come with challenges:
- Traffic Congestion: High traffic in popular areas can lead to delays and require careful navigation.
- Weather Variability: Sailors must remain vigilant about changing weather patterns that can affect their journey.
- Logistical Planning: Routes involving canals or ports may require more extensive planning regarding fees and schedules.
In summary, the choice of sailing route is a critical factor in determining the time and experience of a global sailing journey. By understanding the various routes, their advantages, and challenges, sailors can better prepare for their adventure around the world.
What Is the Traditional Clipper Route?
The Traditional Clipper Route is a historic maritime pathway that has been utilized by sailing vessels for centuries. This route, known for its favorable winds and currents, remains a favored choice for modern sailors looking to circumnavigate the globe efficiently.
The Clipper Route is characterized by its strategic positioning that takes advantage of the prevailing westerly winds found in the Southern Hemisphere. These winds, known as the Roaring Forties, provide an incredible boost to sailing vessels, allowing them to travel faster and more efficiently. The route typically begins in the Atlantic Ocean, passes through the Southern Ocean, and returns through the Pacific Ocean.
While there are several routes available for circumnavigation, the Clipper Route stands out due to its combination of speed and safety. Unlike routes that may require navigating through narrow straits or congested shipping lanes, the Clipper Route offers open waters, minimizing the risks associated with heavy traffic. This makes it particularly appealing for long-distance sailors seeking a more straightforward journey.
- Weather Variability: While the route offers favorable winds, sailors must remain vigilant about sudden weather changes, including storms that can arise unexpectedly.
- Navigation Skills: Mastering the art of navigation is crucial, as the vastness of the ocean can lead to disorientation without proper skills.
- Physical Demands: The journey can be physically taxing, requiring sailors to be in good health and prepared for the rigors of long voyages.
The benefits of sailing the Clipper Route are numerous. Firstly, the speed at which sailors can complete their journey is significantly enhanced by the favorable winds. Additionally, the route allows for a more direct path to various ports of call, reducing overall travel time. Finally, the experience of sailing through some of the world’s most pristine waters is a major draw for many adventurers.
While the Clipper Route is appealing, it is essential to consider the experience level of the sailor. Experienced sailors may find the route manageable and exhilarating, while novice sailors may face challenges that could lead to delays. Proper training and preparation are vital for anyone considering this route.
Preparation is key for a successful journey on the Clipper Route. Here are some essential steps to consider:
- Research Weather Patterns: Understanding seasonal weather changes can help in planning the best time to embark on the journey.
- Equip Your Vessel: Ensure your boat is equipped with the necessary safety gear, navigation tools, and communication devices.
- Build a Strong Crew: Having a reliable and skilled crew can enhance safety and efficiency during the journey.
In conclusion, the Traditional Clipper Route offers a captivating blend of adventure and efficiency for those looking to sail around the world. By understanding its unique characteristics and preparing adequately, sailors can enjoy a remarkable journey across the oceans.
How Do Alternative Routes Impact Duration?
When planning a sailing journey around the world, one of the crucial decisions involves selecting the right route. Alternative routes, such as the Panama and Suez Canals, can significantly influence the overall duration of the voyage. While these canals offer the advantage of saving time, they also come with their own set of considerations that sailors must take into account.
- Time Efficiency: Both the Panama and Suez Canals allow vessels to bypass lengthy detours, drastically reducing travel time.
- Fuel Savings: Shorter routes mean less fuel consumption, which can lead to lower operational costs.
- Access to Key Trade Routes: These canals connect major shipping lanes, making it easier to access global markets.
While the time savings can be substantial, sailors should be aware of the fees involved in using these canals. For instance, transit fees for the Panama Canal can range from a few thousand to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on the size and type of vessel. Similarly, the Suez Canal imposes fees based on the vessel’s tonnage. It is essential to factor these costs into the overall budget for the journey.
In addition to fees, logistical planning is critical when considering alternative routes. Sailors must account for:
- Scheduling: Both canals have specific transit schedules, and waiting times can vary. Planning ahead is essential to avoid delays.
- Documentation: Proper paperwork and permits are necessary for canal transit, which can require time to arrange.
- Weather Considerations: Weather patterns can impact the safety and timing of canal crossings, necessitating careful monitoring.
While alternative routes offer advantages, they also come with inherent risks. Navigating through busy shipping lanes can increase the likelihood of encountering other vessels, necessitating heightened vigilance. Additionally, there may be security concerns in certain regions, making it imperative for sailors to stay informed about local conditions.
Choosing to sail through alternative routes can lead to a faster journey compared to traditional paths, such as the long route around Cape Horn. However, the decision should be based on a balance of time savings, costs, and potential risks. Each sailor’s priorities will dictate the best route for their specific journey.
In conclusion, while exploring alternative routes like the Panama and Suez Canals can save valuable time during a global sailing journey, careful consideration of fees, logistical planning, and associated risks is essential. By weighing these factors, sailors can make informed decisions that enhance their overall sailing experience.

What Is the Average Time to Sail Around the World?
Sailing around the world is a dream for many adventurers, but one of the most pressing questions is: The answer to this question is not straightforward, as it varies significantly based on several key factors.
On average, most sailors complete a circumnavigation in a time frame of 1 to 5 years. This variation largely depends on the sailor’s experience, the type of vessel, and the chosen route.
Experienced sailors often have a more efficient approach to navigation and decision-making, which can reduce the overall time needed for the journey. Typically, these seasoned mariners can finish their circumnavigation in about 1 to 3 years. They are adept at handling unexpected challenges and can make quicker adjustments to their plans.
In contrast, novice sailors may take significantly longer to complete their journey, often ranging from 3 to 5 years. The learning curve associated with long-distance sailing can lead to delays as they encounter new challenges and gain confidence on the water.
The type of boat used for the journey also plays a crucial role in determining the time required. For instance, racing yachts are designed for speed and can cover distances more quickly than traditional cruising sailboats. Catamarans, known for their stability and speed, can also shorten the overall duration of a circumnavigation.
The chosen sailing route is another significant factor. Popular routes such as the Clipper Route provide favorable winds and currents, potentially reducing travel time. Conversely, alternative routes like those through the Panama or Suez Canals can save time but may involve additional logistical considerations.
Weather conditions can significantly impact sailing time. Sailors must be acutely aware of seasonal weather patterns, as these can dictate the best times to set sail and the safest routes to take. Storms and adverse weather systems can lead to detours, extending the journey duration.
Thorough preparation is essential for a successful circumnavigation. This includes equipping the vessel with the necessary navigation tools and safety gear. A well-prepared crew can enhance sailing efficiency and safety, ultimately affecting the time taken to complete the journey.
- Underestimating Time: Many sailors miscalculate the time needed due to unforeseen circumstances.
- Ignoring Weather Patterns: Failure to account for changing weather can lead to dangerous situations and delays.
- Lack of Preparation: Inadequate planning can result in equipment failures and safety issues.
In conclusion, estimating the average time to sail around the world involves a complex interplay of factors, including experience, boat type, route selection, weather conditions, and thorough preparation. By understanding these elements, sailors can better estimate their journey duration and plan accordingly.
How Long Do Experienced Sailors Typically Take?
Sailing around the world is a dream for many adventurers and seasoned sailors alike. However, the time it takes to complete such a journey can vary significantly based on several factors. Experienced sailors often complete the journey in about 1 to 3 years, but this timeframe can fluctuate based on their chosen route and sailing style.
The time taken by experienced sailors to circumnavigate the globe can depend on a multitude of factors. Here are some key considerations:
- Route Selection: The route a sailor chooses can greatly affect the duration of the journey. Traditional routes like the Clipper Route may offer favorable winds and currents, while alternative routes might save time but require careful planning.
- Sailing Style: Some sailors prefer a leisurely pace, taking time to explore various ports and islands, while others may adopt a more direct approach, focusing solely on completing the circumnavigation.
- Weather Patterns: Experienced sailors are adept at reading weather conditions and adjusting their routes accordingly. This skill can significantly impact travel time, as they can avoid storms and unfavorable winds.
Experience plays a crucial role in how quickly sailors can navigate the seas. Experienced sailors tend to be more skilled in:
- Navigation: Proficient sailors are familiar with navigation tools and techniques, allowing them to plot efficient courses and make quick decisions.
- Maintenance: Knowing how to maintain their vessel can prevent delays caused by mechanical issues, ensuring a smoother journey.
- Weather Adaptation: Experienced sailors can better predict weather changes and adjust their sailing plans, which can save time and enhance safety.
The average distance covered by experienced sailors can also influence their overall journey duration. Depending on the route, sailors may cover approximately 20,000 to 30,000 nautical miles. This distance can be achieved in various ways:
| Route Type | Average Distance (Nautical Miles) | Estimated Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Clipper Route | Around 25,000 | 1-2 Years |
| Panama Canal Route | About 20,000 | 1-1.5 Years |
| Exploratory Routes | Varies | 2-3 Years |
Each sailor has unique goals that can affect their journey length. Some may prioritize exploration, while others aim for speed. This divergence in objectives can lead to varying timelines:
- Explorers: Those who wish to explore numerous ports and engage with local cultures may take longer, savoring each stop along the way.
- Direct Sailors: Sailors focused on completing the journey as quickly as possible may opt for fewer stops and more direct routes, thereby shortening their timeline.
In summary, while experienced sailors can complete a circumnavigation in about 1 to 3 years, the actual duration is influenced by route selection, sailing style, personal goals, and weather conditions. Each journey is unique, shaped by the sailor’s choices and experiences.
What About Novice Sailors and Their Time Estimates?
Embarking on a journey around the world by sail is a thrilling adventure that requires careful planning and preparation. For novice sailors, the timeline to complete such a journey can be quite different from that of seasoned mariners. Understanding the challenges they face is essential in estimating how long it may take them to navigate the vast oceans.
Novice sailors often encounter a steep learning curve as they adapt to the complexities of sailing. This includes mastering navigation, understanding weather patterns, and handling the boat in various sea conditions. These challenges can extend their journey significantly, often taking 3 to 5 years to complete a circumnavigation.
Experience plays a crucial role in sailing efficiency. Novice sailors may spend extra time learning essential skills such as:
- Navigation: Understanding charts and using navigational instruments can take time to master.
- Weather Interpretation: Recognizing weather patterns and making decisions based on forecasts is vital for safety and speed.
- Boat Handling: Gaining proficiency in maneuvering the boat, especially in challenging conditions, is a skill that develops over time.
To minimize the time taken to sail around the world, novice sailors can engage in various training programs. These programs often include:
- Formal Sailing Courses: Many sailing schools offer comprehensive courses that cover both theoretical and practical aspects of sailing.
- Hands-On Experience: Joining sailing clubs or participating in crewed charters can provide valuable experience.
- Mentorship: Learning from experienced sailors can accelerate the learning process and provide insights that books cannot.
Effective planning can significantly impact the duration of a sailing journey. Novice sailors should consider:
- Route Selection: Choosing a well-established route can provide favorable conditions and reduce travel time.
- Seasonal Timing: Departing during optimal weather seasons can enhance safety and speed.
- Pre-Departure Preparation: Ensuring the boat is well-equipped and in top condition before setting sail can prevent delays.
Engaging with the sailing community can also benefit novice sailors. Connecting with other sailors through forums, local clubs, and social media can provide:
- Resources: Access to valuable information, tips, and shared experiences.
- Networking: Opportunities to meet potential crew members or mentors who can assist in the journey.
- Encouragement: Emotional support from fellow sailors can help maintain motivation throughout the challenges.
In conclusion, while novice sailors may take longer to sail around the world, the journey can be immensely rewarding. By investing in training, planning meticulously, and engaging with the sailing community, they can enhance their skills and potentially shorten their journey time. Ultimately, sailing is not just about reaching the destination; it’s also about the experiences and lessons learned along the way.

What Are the Key Preparations for a Global Sailing Journey?
Embarking on a global sailing journey is an exhilarating adventure, but it requires meticulous planning and preparation. Before setting sail, understanding the essential preparations can greatly influence the success and enjoyment of your voyage. This section delves into the key preparations necessary for a safe and efficient circumnavigation of the globe.
Having the right equipment is crucial for any long-distance sailing journey. Here are some essential items:
- Navigation Tools: A reliable GPS system and nautical charts are vital for plotting your course and avoiding hazards.
- Safety Gear: Life jackets, flares, and a first aid kit should always be on board to ensure safety in emergencies.
- Communication Devices: A VHF radio and satellite phone are essential for staying in touch with the shore and other vessels.
- Emergency Equipment: An EPIRB (Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacon) can be a lifesaver in distress situations.
Having a well-trained crew is one of the most critical factors in ensuring a smooth sailing experience. Experience can significantly enhance efficiency and safety, impacting the overall duration of the journey. Consider the following:
- Skill Levels: Crew members should possess basic sailing skills, including navigation, watchkeeping, and emergency procedures.
- Teamwork: A cohesive crew can work together seamlessly, allowing for quicker decision-making and problem-solving.
- Training Programs: Enroll in sailing courses to improve skills and knowledge about handling various sailing conditions.
Budgeting for a global sailing journey is essential. Consider the following financial aspects:
- Initial Investment: Costs include purchasing or renting a boat, equipping it with necessary gear, and any modifications needed for long-distance sailing.
- Ongoing Expenses: Fuel, maintenance, food, and docking fees can add up quickly, so it’s important to plan accordingly.
- Insurance: Comprehensive insurance coverage for the boat and crew is vital to protect against unforeseen events.
Planning your sailing itinerary is crucial for a successful journey. Here are some tips:
- Research Destinations: Identify key ports and destinations you wish to visit, considering weather patterns and seasonal conditions.
- Flexibility: Allow for changes in your itinerary based on weather conditions or unforeseen circumstances.
- Time Management: Estimate travel times between ports to ensure you have enough time to explore each location.
Ensuring the health and safety of the crew is paramount. Here are some preparations to consider:
- Health Checkups: Ensure all crew members have necessary vaccinations and medical checkups before departure.
- Emergency Plans: Develop a clear plan for medical emergencies, including access to medical facilities at various ports.
- Safety Drills: Conduct regular safety drills to prepare the crew for emergencies, ensuring everyone knows their roles.
In conclusion, thorough preparations for a global sailing journey are essential for ensuring safety and efficiency. By focusing on the right equipment, crew training, financial planning, itinerary creation, and health preparations, sailors can significantly enhance their overall experience and navigate the challenges of circumnavigating the globe.
What Equipment Is Necessary for Long-Distance Sailing?
When planning a long-distance sailing journey, having the right equipment is vital for ensuring safety and enhancing the overall experience. Proper preparation can significantly impact the success of a circumnavigation, making it essential to understand what tools and gear are necessary.
Effective navigation is crucial for any sailor. The following tools are indispensable:
- GPS Devices: These provide real-time positioning, helping sailors stay on course.
- Charts and Maps: Traditional paper charts are still important for backup and understanding coastal features.
- Compasses: A reliable compass is essential for determining direction, especially when electronic devices fail.
- Autopilot Systems: These help maintain a steady course, allowing sailors to manage other tasks.
Safety gear is non-negotiable for long voyages. Key items include:
- Life Jackets: Every crew member should have a properly fitted life jacket.
- Emergency Beacons: Devices like EPIRBs (Emergency Position Indicating Radio Beacons) are crucial for distress signaling.
- First Aid Kits: A well-stocked first aid kit can address minor injuries and emergencies.
- Flares and Signaling Devices: These are essential for attracting attention in case of emergencies.
Maintaining communication is vital, especially during long voyages. The following devices should be considered:
- VHF Radio: This is essential for communicating with other vessels and coast stations.
- Satellite Phones: These provide reliable communication even in remote areas where cell service is unavailable.
- SSB Radio: Single Sideband radios are useful for long-range communication.
Beyond navigation and safety, certain equipment can enhance the comfort and efficiency of a long-distance journey:
- Watermakers: These devices convert seawater into fresh water, ensuring a continuous supply.
- Solar Panels: Utilizing solar energy can help power onboard electronics and reduce reliance on fuel.
- Refrigeration Units: Keeping food fresh is crucial during long trips, making refrigeration systems important.
Regular maintenance of all equipment is crucial. Ensuring that navigation tools, safety gear, and communication devices are in optimal condition can prevent failures during critical moments. Routine checks and servicing can save time and enhance safety, making the journey more enjoyable.
In conclusion, embarking on a long-distance sailing journey requires meticulous planning and the right equipment. From navigation tools to safety gear and communication devices, each piece plays a significant role in ensuring a successful circumnavigation. By investing in quality gear and maintaining it properly, sailors can focus on enjoying the adventure ahead.
How Important Is Crew Experience and Training?
Sailing around the world is a thrilling adventure that requires not only a well-equipped vessel but also a highly trained crew. The experience and training of the crew can dramatically influence various aspects of the journey, including safety, efficiency, and overall sailing performance.
A crew’s experience plays a vital role in ensuring that the sailing journey is successful. Experienced sailors are familiar with the intricacies of navigation, weather patterns, and emergency procedures, which can be crucial when facing unexpected challenges at sea.
Training equips the crew with the necessary skills to operate the vessel efficiently. A well-trained crew can manage sails, navigate, and respond to emergencies swiftly, which ultimately enhances sailing efficiency. This efficiency can lead to a reduction in travel time, allowing for a more streamlined journey.
- Emergency Preparedness: Trained crews are better prepared to handle emergencies such as man-overboard situations or equipment failures.
- Navigation Skills: Knowledge of navigation techniques helps in avoiding hazards and optimizing routes.
- Weather Assessment: Experienced sailors can interpret weather forecasts and make informed decisions to avoid dangerous conditions.
Having a cohesive crew can significantly improve the sailing experience. When crew members work well together, they can communicate effectively and execute maneuvers with precision. This teamwork is particularly important during challenging conditions, where coordination can make a difference between a safe passage and a perilous situation.
Continuous training not only keeps the crew’s skills sharp but also fosters a culture of safety and readiness. Regular drills and educational sessions can help the crew stay updated on the latest sailing techniques and safety protocols. This ongoing commitment to training ensures that the crew is always prepared for the unexpected.
The time taken to sail around the world can vary significantly based on crew experience. A well-trained crew can navigate more efficiently, avoid potential pitfalls, and make quicker decisions, which can reduce overall travel time. In contrast, an inexperienced crew may take longer to complete the journey, as they may need to spend additional time learning and troubleshooting.
Leadership on board is crucial for maintaining morale and ensuring that all crew members are working towards a common goal. An experienced captain can inspire confidence, delegate tasks effectively, and make strategic decisions that enhance the overall performance of the crew. This leadership is essential in high-pressure situations, where quick thinking can prevent disasters.
Before setting sail, it’s important to invest time in crew training. This can include:
- Workshops: Conducting workshops on navigation, weather patterns, and emergency procedures.
- Simulations: Engaging in simulated sailing scenarios to practice responses to various situations.
- Team-Building Activities: Organizing activities that enhance teamwork and communication among crew members.
In conclusion, crew experience and training are fundamental to a successful sailing journey around the world. By investing in the development of a skilled and cohesive crew, sailors can enhance their efficiency and safety, ultimately influencing the time taken to complete their adventure.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How long does it take to sail around the world?
The time it takes to sail around the world varies widely, typically ranging from 1 to 5 years. Experienced sailors may complete the journey in about 1 to 3 years, while novices might take longer due to learning curves.
- What factors can affect my sailing time?
Several factors influence sailing duration, including boat type, weather conditions, and chosen routes. For instance, catamarans often sail faster than monohulls, and favorable weather can significantly shorten the journey.
- What are the best routes for circumnavigation?
The traditional Clipper Route is popular for its favorable winds, but alternative routes like the Panama or Suez Canals can save time. Each route has its unique challenges and benefits.
- How important is crew experience?
Having a well-trained crew is crucial for safety and efficiency. Experienced crew members can navigate challenges better, ultimately affecting the overall time taken for the journey.
- What equipment do I need for long-distance sailing?
Essential equipment includes navigation tools, safety gear, and communication devices. Proper gear ensures a smoother journey and can help avoid delays due to equipment failures.




